FIND-S: FINDING A MAXIMALLY SPECIFIC HYPOTHESIS
FIND-S: FINDING A MAXIMALLY SPECIFIC HYPOTHESIS
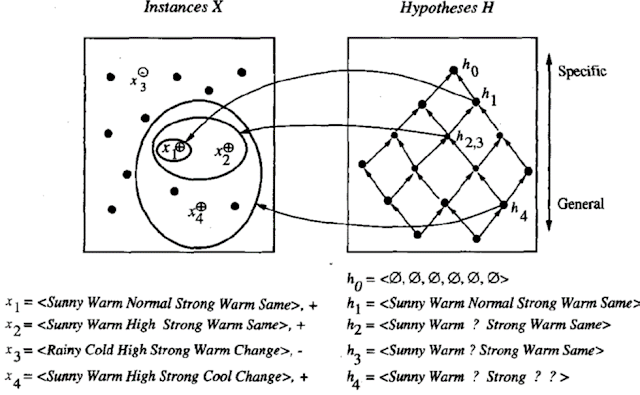
• To illustrate this algorithm, assume the learner is given the sequence of training examples from the EnjoySport task.
Step 1: Initialize h to the most specific hypothesis in H
·
The first step of FIND-S is
to initialize h to the most specific hypothesis in H
h - (Ø, Ø, Ø, Ø, Ø, Ø)
·
Consider the first training example
x1 = <Sunny, Warm, Normal,
Strong, Warm, Same>, +
•
Observing the first training example, it is clear that hypothesis
h is too
specific.
None of the "Ø" constraints in h are satisfied by
this example, so each is replaced by the next more general constraint that fits the
example
h1 = <Sunny, Warm,
Normal, Strong, Warm, Same>
·
Consider the second training example
x2 = <Sunny, Warm, High,
Strong, Warm, Same>, +
•
The second training example forces the algorithm to further
generalize h, this time substituting a "?" in place of any attribute value in h that
is not
satisfied by
the new example
h2 = <Sunny, Warm, ?,
Strong, Warm, Same>
· Consider the third training example
x3 = <Rainy, Cold, High,
Strong, Warm, Change>, -
•
Upon encountering the third training the algorithm makes no
change to h. The FIND-S algorithm simply ignores every negative example.
h3 = < Sunny Warm ?
Strong Warm Same>
·
Consider the fourth training example
x4 = <Sunny Warm High
Strong Cool Change>, +
•
The fourth example leads to a further generalization of h
h4 = < Sunny Warm ?
Strong ? ? >
The key property of the FIND-S algorithm
·
FIND-S is guaranteed to output the most specific hypothesis within H that is
consistent with the positive training examples
·
FIND-S algorithm’s final hypothesis will also be consistent with
the negative examples provided the correct target concept is contained in H,
and provided the training examples are correct.








Comments
Post a Comment