Naive Bayes Classifier - Example -classify- play tennis - forecast
Naïve Bayes Classifier - Example -classify- play tennis - forecast
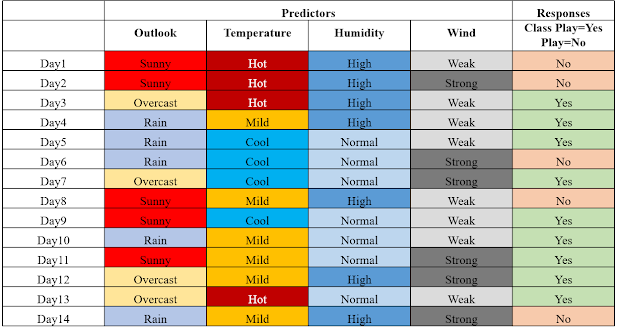
- Let’s build a classifier that predicts whether I should play tennis given the forecast.
- It takes four attributes to describe the forecast; namely,
- the outlook,
- the temperature,
- the humidity, and
- the presence or absence of wind.
- Furthermore, the values of the four attributes are qualitative (also known as categorical).
- They take on the values shown below.
- 𝑶𝒖𝒕𝒍𝒐𝒐𝒌 ∈[𝑺𝒖𝒏𝒏𝒚,𝑶𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒂𝒔𝒕, 𝑹𝒂𝒊𝒏𝒚]
- 𝑻𝒆𝒎𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒆∈[𝑯𝒐𝒕,𝑴𝒊𝒍𝒅, 𝑪𝒐𝒐𝒍]
- 𝑯𝒖𝒎𝒊𝒅𝒊𝒕𝒚 ∈[𝑯𝒊𝒈𝒉, 𝑵𝒐𝒓𝒎𝒂𝒍]
- 𝑾𝒊𝒏𝒅𝒚 ∈[𝑾𝒆𝒂𝒌, 𝑺𝒕𝒓𝒐𝒏𝒈]
- The class label is the variable, Play and takes the values Yes or No.
- 𝑷𝒍𝒂𝒚∈[𝒀𝒆𝒔, 𝑵𝒐]
- We read-in training data below that has been collected over 14 days
Classification Phase
Let’s say, we get a new instance of the weather condition,
𝑿^′=(𝑶𝒖𝒕𝒍𝒐𝒐𝒌=𝑺𝒖𝒏𝒏𝒚, 𝑻𝒆𝒎𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒆=𝑪𝒐𝒐𝒍, 𝑯𝒖𝒎𝒊𝒅𝒊𝒕𝒚=𝑯𝒊𝒈𝒉, 𝑾𝒊𝒏𝒅=𝑺𝒕𝒓𝒐𝒏𝒈)
that will have to be classified (i.e., are we going to play tennis under the conditions specified by 𝑋^′).
With the MAP rule, we compute the posterior probabilities.
This is easily done by looking up the tables we built in the learning phase.








Comments
Post a Comment